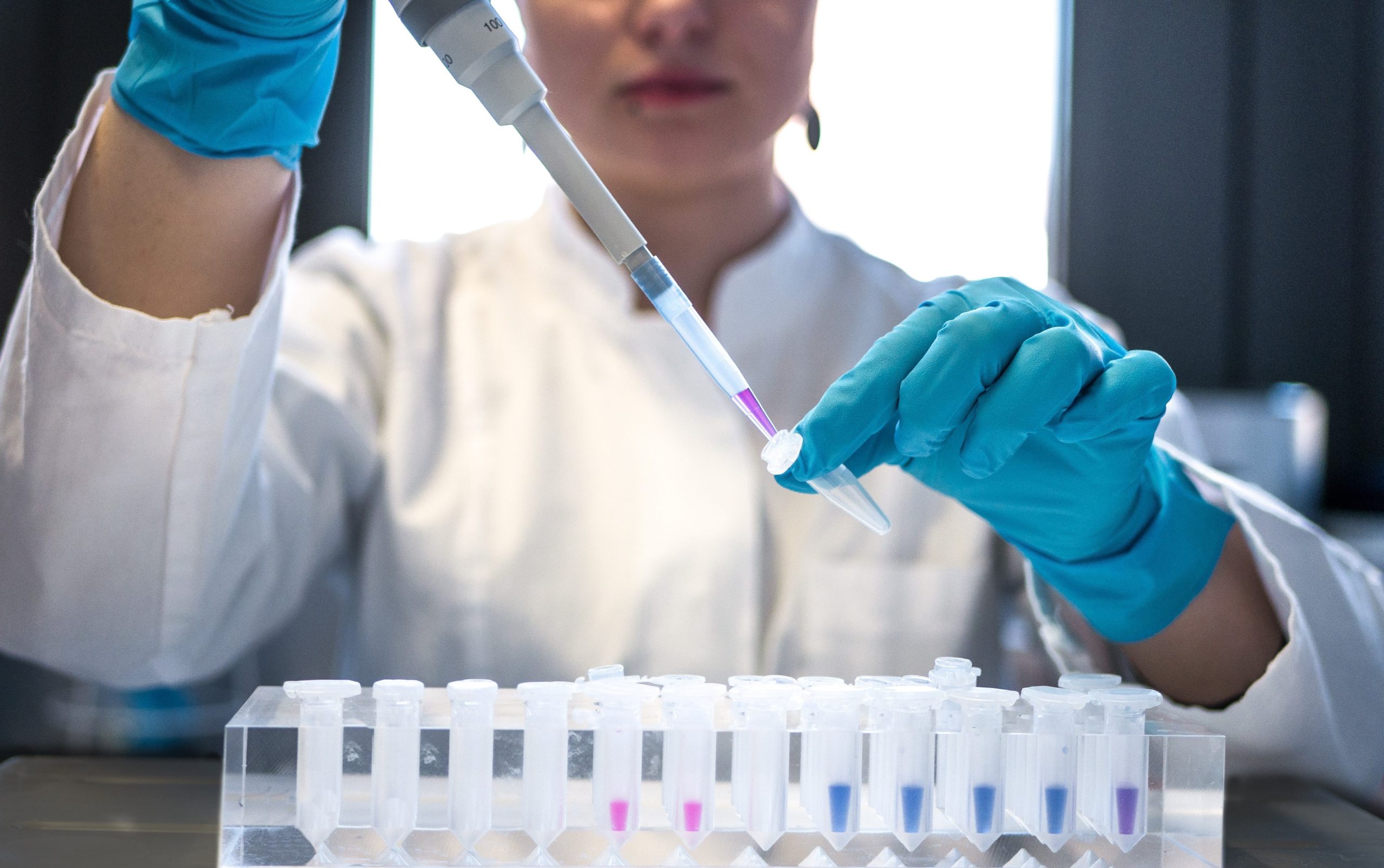
In the realm of botanical science, the extraction of natural products from plants plays a pivotal role across various industries, including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food. The growing consumer preference for organic and natural products has fueled the demand for natural extracts, prompting the development of more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective extraction methods. Recent advancements in botanical extraction methods, particularly the introduction of innovative solvents, are revolutionizing the way essential oils, flavors, medicinal compounds, and other valuable phytochemicals are obtained from plants.
Traditional extraction methods have long been plagued by limitations such as low efficiency, high energy consumption, and the use of toxic solvents, which can compromise the quality and purity of extracted compounds and pose environmental and health risks. The current revolution in botanical extraction technologies aims to address these issues by offering greener, cleaner, and more effective solutions.
One of the key innovations in botanical science is the advent of green solvents in the extraction process. Unlike conventional solvents, green solvents are derived from renewable resources and exhibit low toxicity, making them environmentally friendly and safe for various applications. Popular green solvents include supercritical CO2, ionic liquids, deep eutectic solvents (DES), and bio-derived solvents like ethanol obtained from biomass.
Supercritical CO2 extraction, in particular, has gained recognition for its efficiency in extracting high-quality essential oils and active compounds. This process is solvent-free, as CO2 can be easily removed by depressurization, resulting in pure extracts without any solvent residues, unlocking the valuable phytochemicals found in plants for various uses.
Ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents are considered next-generation solvents that offer versatility and eco-friendly characteristics. These solvents exhibit unique solvating properties that can be customized to target specific compounds, enhancing the extraction process’s selectivity and efficiency while reducing waste and environmental impact.
Technological advancements have also given rise to novel extraction techniques like ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and microwave-assisted extraction (MAE). These methods utilize ultrasonic waves and microwave radiation, respectively, to facilitate the extraction of natural products, resulting in reduced extraction times, lower solvent consumption, and enhanced yields.
Enzyme-assisted extraction is another innovative approach that uses specific enzymes to break down plant cell walls and increase cell membrane permeability, improving the extraction of valuable compounds while minimizing damage to active ingredients. These advancements in botanical science represent a significant leap forward in natural product extraction technologies, promising greener, more efficient methods that could revolutionize how we harness plants’ power.
As the demand for natural and organic products continues to rise, these innovations in botanical science are poised to play a crucial role in meeting consumer expectations and driving the sustainability agenda forward. By focusing on sustainability, efficiency, and safety, cutting-edge extraction technologies are not only enhancing the quality of natural extracts but also contributing to a healthier planet and a brighter future for industries reliant on botanical resources.